BSE

Information applies to products distributed in the United
States. For international availability please![]() click here or visit your country's Abbott web site listed
under the Worldwide menu.
click here or visit your country's Abbott web site listed
under the Worldwide menu.
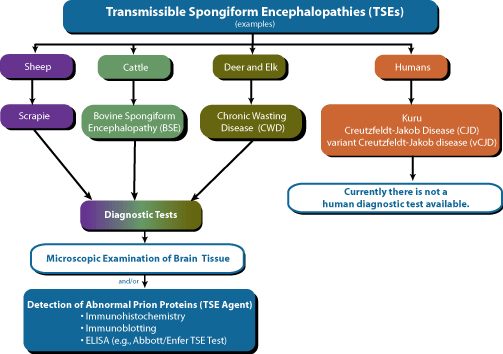
TSE Screening Process
With the transmission of mad cow disease or BSE to humans in the form of vCJD, there has been a significantly increased awareness of TSEs and their potential threat to human health. This increased concern for the threat to human health has been accompanied by a call for more testing to determine the true incidence of these diseases, especially in animals that pose a possible source of infection to humans.
One way to test for TSEs is via the detection of the abnormal prion proteins by immunological methods. Because of the large number of samples involved and the relative rapidity of the test, an ELISA format is clearly beneficial.1
The Abbott/Enfer TSE Test
Easy
Designed for mass screening; capable of testing up
to 8,000 samples daily
Fast
Assay time 3.5 hours including Sample
preparation
Reliable
To date in excess of 3 million animals tested in
Europe
Safe
European Commission Validated as 100% sensitive and
100% specific in detecting BSE
Proven ability to detect sub-clinical and
pre-symptomatic cases
Redundant sampling ensures specificity and
reliability
- More Information on Enfer Scientific
- Video presentation about the Abbott/Enfer TSE Test
Windows Media Player: Broadband or Dial-Up (Download Windows Media Player)
RealPlayer: Broadband or Dial-Up (Download RealMedia Player)
How Does the Abbott/Enfer TSE Test for BSE Work?
Sample Collection
A sample of bovine central nervous
tissue is dissected from the hind brain (including the Obex region) or upper
cervical spinal column. The sample is placed in a transport carrier and
transported to a laboratory for analysis.
Sample Preparation for Immunoassay Analysis
Laboratory
technicians use a unique sampling device to obtain the correct amount of sample,
between 0.5 grams and 1.0 grams (preferably from the Obex region of the brain).
The sample is collected using a safe and easy tool provided with each kit.
Special care is taken to ensure that the sample contains gray matter since this
has the greatest concentration of prions. The sample and a special buffer are
placed in an easy–to-use homogenizer bag and subjected to a gentle
homogenization. The approximately two-minute homogenization process ensures that
the tissue is broken down and the prions are solubilized.
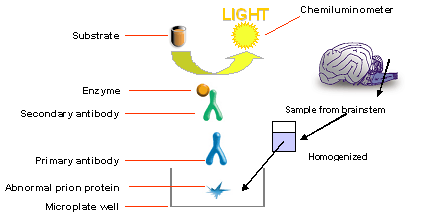
After homogenization, the liquid homogenate is centrifuged. The supernatant of the sample is transferred to a multiple-well plate containing a special enzyme solution called Proteinase K. During incubation, Proteinase K digests the normal prion proteins in the sample, while the abnormal prion proteins (BSE agent) remain intact and bind to the sample well. The sample is now ready for the immunoassay procedure.
Immunoassay Procedure
A denaturation step follows the
adsorption of the BSE agent to the sample well. After washing, the primary
antibody is added and allowed to bind to the BSE agent adsorbed to the sample
well. After washing away the excess primary antibody, a secondary antibody is
added and allowed to bind to the primary antibody-BSE agent complex. After
washing away any unbound secondary antibody, a chemiluminescent substrate
solution is added, which detects the presence of the secondary antibody and
emits a luminescent signal. The signal, which is proportional to the presence of
BSE agent in the sample, is read with the appropriate chemiluminescent
analytical equipment.
References
- Klass MR, Hodges S, Sayers R, et al. A test for transmissible spongiform encephalopathy. Am Biotechnol Lab 2002, 20(12)34–36.
This Test is associated with this Medical Condition(s):